Rotation-based devices, such as thermostats and joysticks, need an accurate reading of angular displacements to measure rotation angle. Though mechanical contacts can do the job, their performance can be limited by continuous mechanical friction or dirt and grime. In this regard, hall effect sensors act as an ideal contactless sensing alternative. The use of inductive and capacitive sensors is also common. While inductive sensors can best detect metal objects- except iron-based, capacitive inductance is helpful for human touch and proximity detection.
Azoteq’s IQS624 is the world’s first hall rotation sensor with multifunctional inductance and capacitance sensors– all in a single, low-profile DFN (3×3)-10 package. The sensor finds its application in designing a contactless and waterproof magnetic knob and inductive buttons such as mouse wheel, selector knob, thermostat, and digital angle gauge. The On-chip Hall plates can sense the angle of the magnet in perpendicular or parallel to the sensor at 1° resolution. A standard I2C interface enables multi-master and multi-slave communication with a low pin/signal count. The IC calculates and streams the current magnet angle without any extra equipment.
Amidst so many USPs, understanding the IQS624 datasheet will help you better acknowledge its robust, high-performance combination sensing for digital crown wheels.
Analyzing IQS624 Datasheet
Pins and Packages
IQS624 belongs to Azoteq’s ProxFusion® sensor series- a proprietary combined sensor solution. The sensor is available in DFN(3×3)-10 and WLCSP-9 packages.
The layout of the pins and their descriptions are shown below.
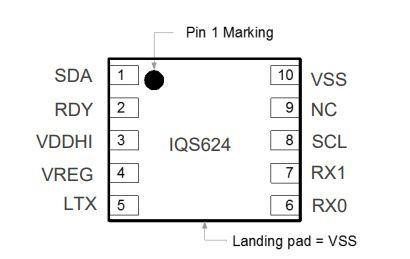
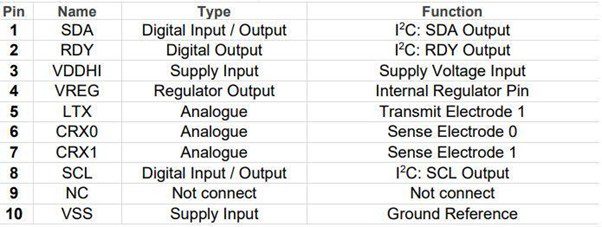
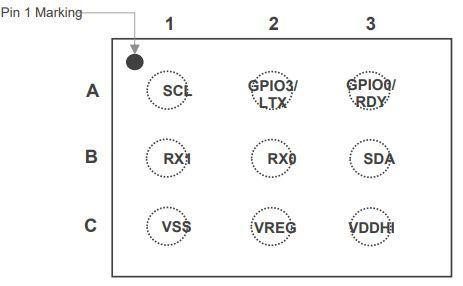
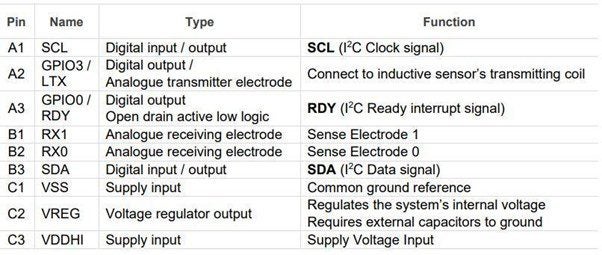 For more information on device marking and ordering information, you can refer to the IQS624 datasheet from Azoteq.
For more information on device marking and ordering information, you can refer to the IQS624 datasheet from Azoteq.
Absolute Maximum Specifications
The device has absolute maximum ratings, as shown in the table below.
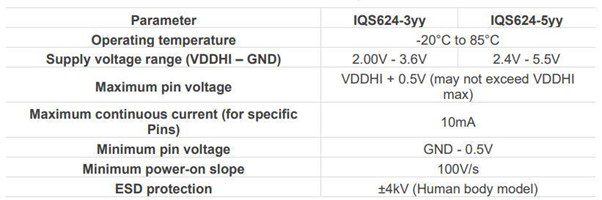
Alt Text: IQS624 Absolute Maximum Ratings
Sensors
The below table shows the sensor-channel association for IQS624. 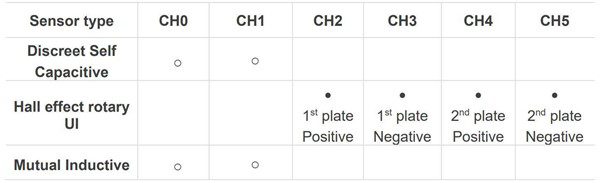 As you can see, a maximum of two channels are available for configuring the capacitive sensor. To obtain the desired sensitivity, you can select the proximity and touch threshold for each channel.
As you can see, a maximum of two channels are available for configuring the capacitive sensor. To obtain the desired sensitivity, you can select the proximity and touch threshold for each channel.
Similarly, you can configure inductive sensing capabilities using the same two channels dedicated for capacitive sensing. You require three sensing lines- one from supply input and the rest from dedicated channels.
Apart from two optional channels for capacitive and inductive sensing, the IC has four more explicitly dedicated to configuring the hall effect sensor. Two internal hall-effect sensing plates are present inside to convert the potential difference measured into current using an operational amplifier. The same data is fed into the ProxSense® sensor engine to calculate absolute position in degrees.
Angle Calculation
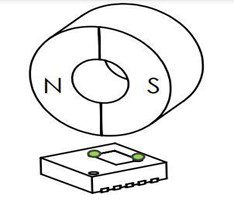
There are two general applications of IQS624 hall sensors:
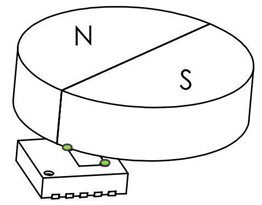
- Absolute off-axis hall rotation sensor: The angle sensor is centered to the side of the rotating magnet. Ex: mouse wheel, revolution counter, measuring wheel, etc.
- Relative on-axis hall rotation sensor: The angle sensor is centered directly under or over the rotating target magnet. Ex: thermostat control, volume knob, motor PID control, etc.
 |
 |
| On-axis hall sensor | Off-axis hall sensor |
As shown in the images above, two hall sensors inside the chip are located at the two corners of the die (indicated in green colors) with a phase difference of 20º to 50° in between. The potential difference across them due to change in the magnetic field in the z-axis can be used to calculate a phase difference which then can be converted into degrees.
ATI Functionality
One of the tough challenges in configuring capacitive sensors is to tune in the electrodes to similar sensitivity, leading to several design iterations. Azoteq’s novel ATI (Auto Tuning Technology) uses intelligent signal processing to auto-tune the touch sensors against any parasitic object to avoid false reads. The ATI functionality will automatically compensate for any routing layout as well as parasitic capacitance from a hundred femtofarads to a hundred picofarads. You can refer to Appendix C of the IQS624 datasheet for more information on ATI parameters and compensations.
IQS624 Alternatives
IQS624 belongs to Azoteq’s ProxFusion family of solutions. ProxFusion brings ICs with multiple sensor technologies embodied into one chip. The ICs, launched under the first-generation ProxFusion technology, can offer one or many of the following six sensing mechanisms:
- PIR (Passive Infrared Sensing)
- ALS (Ambient Light Sensing)
- HALL (Hall Effect Sensing)
- Active IR (Active Infrared Sensing)
- Capacitive (Capacitive Sensing)
- Inductive (Inductive Sensing)
Azoteq has released six sensors under the first-generation ProxFusion sensor technology, including the IQS624 IC. Each sensor has a uniqueness of on-chip technologies optimized for specific markets. The table below shows different alternatives to IQS624 as per specific sensing technologies requirements.
| Sensor Technology | IQS 620 | IQS 621 | IQS 622 | IQS 624 | IQS 670 | IQS 680 |
| Capacitive | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
| ALS | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| PIR | ✓ | ✓ | ||||
| Active IR | ✓ | |||||
| Inductive | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | |
| Hall | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ | ✓ |
If you are looking for how to best use the IQS624 datasheet for your board design, Ultra Librarian will help you find footprints, application notes, ECAD/MCAD models and sourcing information to avoid supply chain bottlenecks with ease.
Working with Ultra Librarian sets up your team for success to ensure streamlined and error-free design, production, and sourcing. Register today for free.