
Diodes are one of the most commonly used electronic components. The 1N4148 diode is a standard silicone switching signal diode. It is useful for applications up to 100 MHz with a recovery time of fewer than four ns. Thus, it is known for its fast switching properties. The diode finds its application in the gate circuit of transistors, MOSFETs, and IGBTs for fast signal transfer from the IC.
Interestingly, it is a common misconception amongst most designers that the 1N4148 is a Zener diode. While the Zener diode conducts in both directions, the 1N4148 conducts only in the forward biased condition. Thus, a fair understanding of the 1N4148 datasheet and easy access to its footprints, application notes, and ECAD/MCAD models is necessary when leveraging its advantages for legacy circuit designs.
Understanding the 1N4148 Datasheet
Absolute Maximum Ratings
The table below shows the maximum electrical stress the diode can handle.
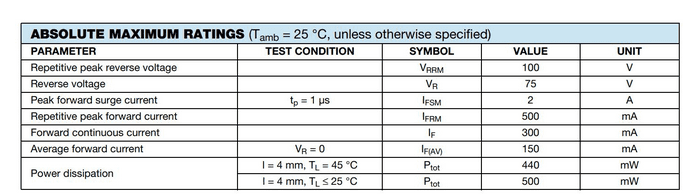
As we can see, this diode can safely handle a maximum spike of 100 V (VRRM) in the reverse direction. However, the maximum voltage drop during the reverse biased condition should not be more than 75 V.
When the diode is forward biased, it can conduct current up to 300 mA (IF) with a peak not more than 500 mA (IFRM) on a continuous basis. But in extreme conditions, it can safely handle a maximum peak current of 2A (IFSM) for not more than 1 μs before breakdown.
Thermal Characteristics
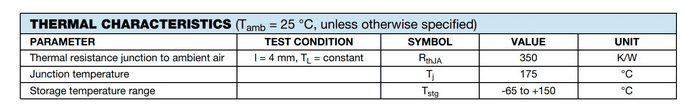
It is imperative to understand thermal characteristics to prevent diode overheating and failure. This diode can dissipate 350 Kelvin heat from the surface of the die to the ambient air via all paths when it consumes 1 watt of power – represented as RthJA in the 1N4148 datasheet. The diode operates safely when the junction temperature is not more than 175°C (Tj).
Electrical Characteristics
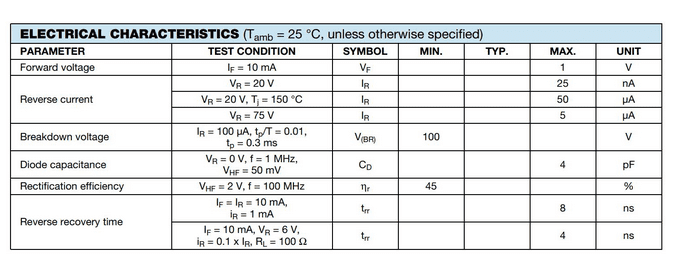
The diode starts to conduct on the application of the minimum forward biased junction voltage of 0.7V. However, in the forward biased condition, the maximum voltage drop across the diode would be 1V for allowing the rated current to pass through it.
The 1N4148 datasheet also lists the maximum value of current that can flow through the diode in the reverse direction (IR) under various test conditions.
The diode enters the breakdown zone when a voltage of 100 V is applied across the terminals in the reverse direction, also known as the breakdown voltage (VBR). Post breakdown, the current flow through the diode grows exponentially and leads to damage.
For every diode, there exists some unwanted self-capacitance (CD) due to the presence of charge particles across the p-n junction and the depletion layer. In the case of 1N4148, this self-capacitance has a maximum value of 4pF. You may have to consider it as an essential design parameter while dealing with high-frequency circuits such as amplifiers and resonators.
When used as a rectifier, the 1N4148 silicon epitaxial planar diode can work at a 45% rectification efficiency (nr). That given, for 100% AC input, the diode produces 45% DC output.
Another important characteristic of this diode is its low reverse recovery time (trr). It represents the time taken by the diode to switch from the forward state to the reverse state in the middle of the operation. Typically, for general diodes, it takes 150ns- 200ns and 20ns for ultra-fast diodes. However, for 1N4148, it takes only 8ns. The 1N4148 datasheet also states the ideal condition to further bring down this time to 4ns. That is a reason the diode has been highly sought-after for fast switching applications.
You will also find some typical performance characteristic graphs helpful for design considerations. Consider the first figure that plots the diode’s forward voltage against relative junction temperature as follows.
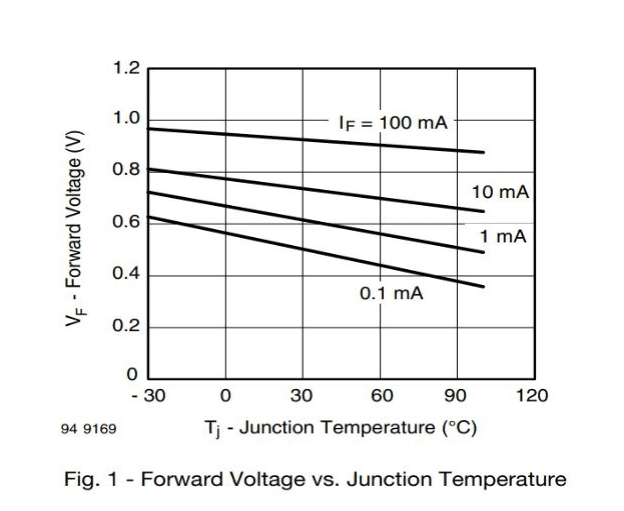
The graph clearly shows the diode achieves breakdown at a lower voltage than under ambient conditions when the temperature is high.
These graphs show how the forward voltage varies indirectly with the junction temperature. A high temperature marks an increase in the vibration of atoms inside the junction. It reduces the mean free path for electrons to travel; hence, a low forward breakdown voltage does the job. Similarly, at low temperatures, the scenario is just the opposite.
Packaging and Dimension
The diode comes in DO-35 semiconductor package. Such packaging is meant for handling small amounts of current and voltage. The package dimension is shown below.
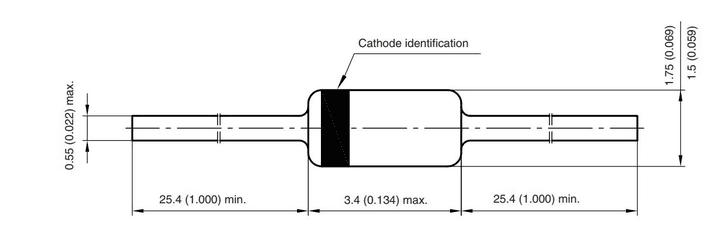
Fig 2 – 1N4148 Diode package dimensions
The 1N4148 diode is a reliable semiconductor that engineers have relied upon for years. However, Vishay Intertechnology no longer offers this diode for new applications. Instead, an alternative component, the 1N4148W–which is RoHS compliant and AEC-101 stress test qualified–is recommended for new designs.
The 1N4148 datasheet should be supported with accurate CAD drawings to best utilize the diode for fast switching applications. Ultra Librarian offers a vast library of data; such as access to datasheets, ECAD models, and simulation and testing information for your ECAD of an electronic component in one place. In addition, to avoid supply chain bottlenecks, you may check for component availability status, price, and models available from different vendors.
Working with Ultra Librarian sets up your team for success to ensure streamlined and error-free design, production, and sourcing. Register today for free.










