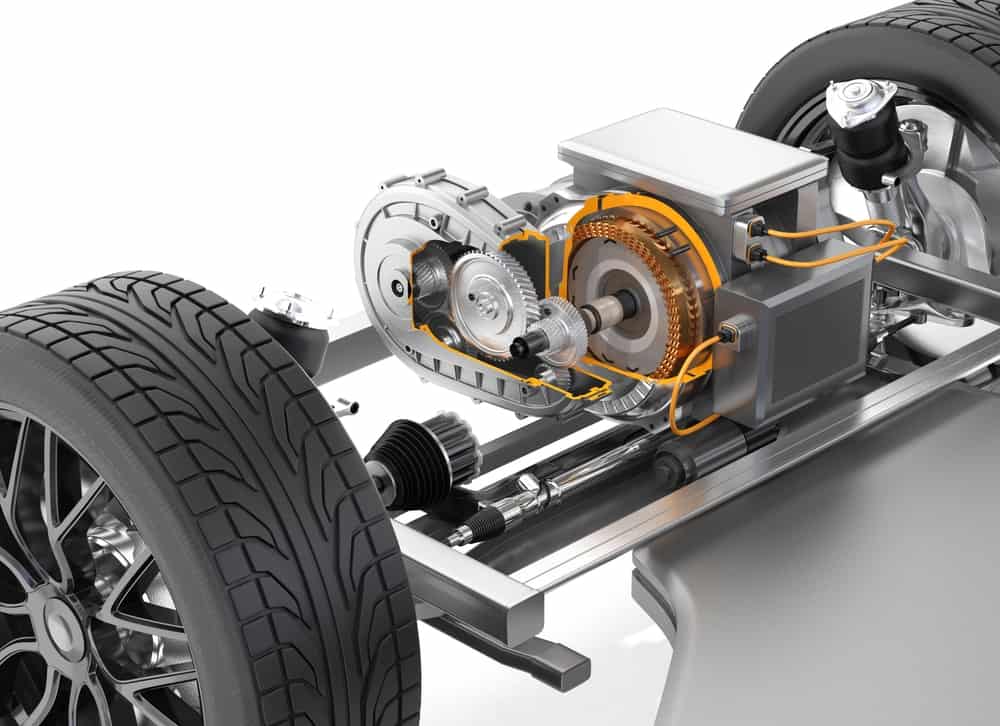

Essential electromechanical components in electric vehicles
The number of parts in an internal combustion car can vary widely, depending on the size and type. Around 30, 000 or so is the average. Electric vehicles require far less. For example, motors for gas-powered cars include around a couple of hundred parts, while EV motors need only about 20. Although, critical for operation, the motor is but one of the essential electromechanical components in electric vehicles.
Types of Electromechanical Components in Electric Vehicles
The group of elements classified as electromechanical components includes any device that includes both electrical and mechanical functionality. Typically, this means a component that uses an electric signal to cause a mechanical action. However, parts that operate in the reverse; such as switches–where the creation of a physical connection causes electric current to flow–are also electromechanical components. In addition to switches, relays, circuit breakers, diodes, solenoids, and transformers are common examples.
A broader definition, where electrical, electronic, and/or mechanical parts that assist or help facilitate electromechanical operation is also common. A number of automotive devices can be categorized in this group. For electric vehicles (EVs), this includes the following common components.
|
COMMON ELECTROMECHANICAL COMPONENTS IN ELECTRIC VEHICLES |
|
|
EM Component Type |
Description |
|
Electric motor |
Converts electrical energy from the battery pack into mechanical energy to drive the motion of the vehicle’s wheels. |
|
Electric transmission |
The transmission is the facilitator between the motor and wheels. in is controlled by electrical energy |
|
Controller |
This device manages the distribution of electric energy that controls mechanical actions like motor torque. |
|
Thermal management |
This system controls the environment temperature that EV components and systems operate in. It may include both electronic and mechanical parts. |
|
Charge port |
Charge ports allow for mechanical connection to external electric energy charging stations to replenish the battery pack. |
|
UI systems |
Displays, switches, door locks, and a host of other user interactive devices are also common. |
The traction battery pack and inverter; although not specifically electromechanical components, are important EV parts. These and the components listed above are common to virtually all EVs. However, electromechanical component requirements vary for different EV types.
EM Component Requirements for Different EVs
EVs are classified as one of the three types shown below.
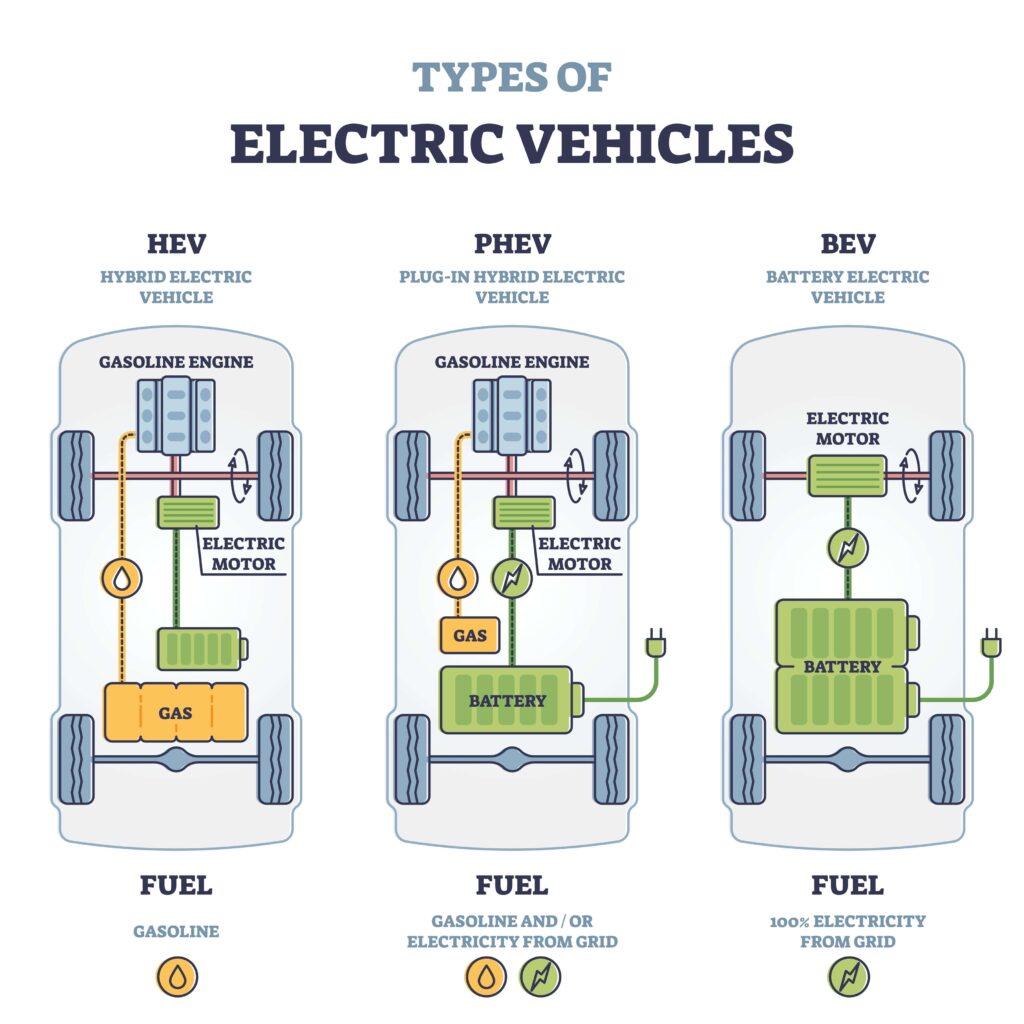
View of different electric vehicle types
In additional to vehicle class distinctions; such as sedan, SUV, etc., EVs are differentiated based on how electric energy is acquired and degree to which it affects operation. As shown above, these classification types are hybrid electric vehicle (HEV), plug-in electric vehicle (PHEV), and battery electric vehicle (BEV). The number and types of electromechanical components required vary based on EV type.
Electromechanical Component in Electric Vehicles Requirements
- HEVs – these EVs are the closest to traditional automotive vehicles and include the electromechanical components typically found in internal combustion vehicles. They do have electric motors, but not charge ports.
- PHEVs – similar to HEVs in that gas operation is still used. However, larger battery packs and charge ports are utilized.
- BEVs – these vehicles are fully electric and the rechargeable battery pack is the only energy source. All electromechanical components common to EVs are included.
Irrespective of the type, there are EV design best practices that should be followed to ensure reliable and safe operation. These include making the best electronic component selections for your design.
Choosing the Best EM Components for Your EV Design
The most important criteria when designing circuit boards for all automotive systems; including EVs, is to be guided by safety considerations. Therefore, it is important to know and adhere to automotive PCB standards. A major aspect of meeting this mandate is choosing the right electromechanical components for your EV board design, which is best accomplished by following guidelines, as listed below.
Electromechanical Components in Electric Vehicles Selection Guidelines
✅ Choose parts that can safely operate in the automotive environment.
Automotive environments can be considered hazardous, especially for electronics. Constant motion, vibration, and extreme temperature swings put tremendous physical and thermal stress and strain on electromechanical components.
✅ Rely on verifiable component data sources.
CAD models, datasheets, product papers, and other publications are essential to create accurate designs. However, it is important to only use information that has been vetted and is verifiable to ensure accuracy.
✅ Only source components from a reliable industry source.
It is also important to source components from reliable vendors. Failing to do so may result in inferior quality or counterfeit components making their way into your your product.
Following guidelines such as those listed above can save you the wasted time and expense that comes with contingencies like inaccurate data and inferior electromechanical components. These potential issues can be eliminated by looking to a trusted industry leader for component models and information.
If you’re looking for CAD models for common components or electromechanical components for electric vehicles, Ultra Librarian helps by compiling all your sourcing and CAD information in one place.
Working with Ultra Librarian sets up your team for success to ensure streamlined and error-free design, production, and sourcing. Register today for free.








