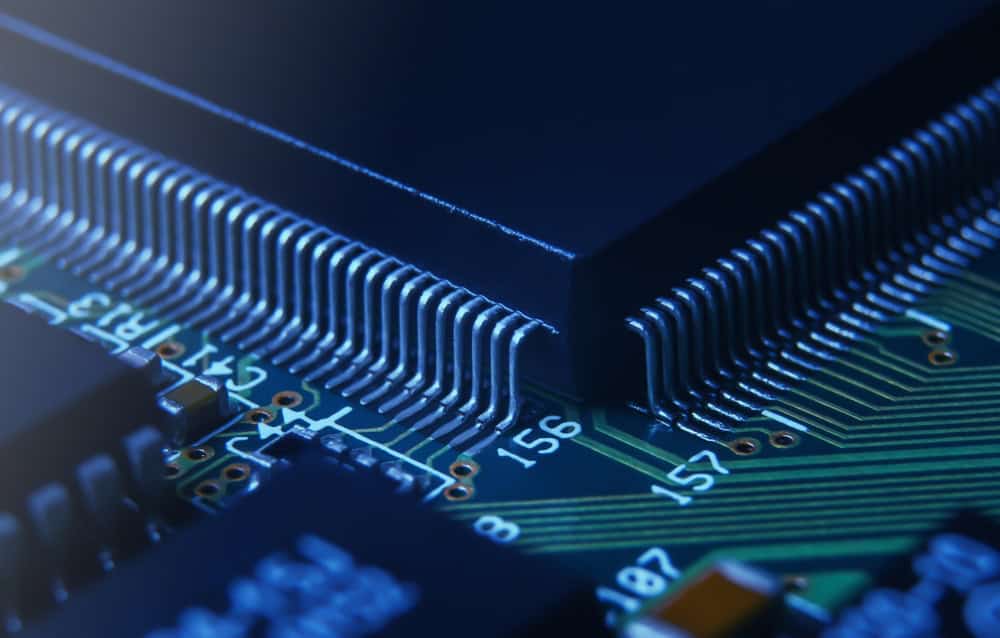
Application-specific integrated circuit in QFP package mounted on PCB
Application-specific integrated circuits (ASICs) are integrated circuits designed for specific purposes within embedded systems. For complex devices like microcontrollers or microprocessors their performance and efficiency are optimized by incorporating specialized hardware accelerators, custom logic, and memory configurations. The table below discusses the various applications of an application-specific integrated circuit in embedded systems.
|
APPLICATION-SPECIFIC INTEGRATED CIRCUITS IN EMBEDDED SYSTEMS: APPLICATIONS |
||
|
Industry |
Devices |
Purpose |
|
Consumer Electronics |
Smartphones, digital cameras, and gaming consoles
|
Specialized functionalities like image processing, audio/video encoding/decoding, and wireless communication protocols |
|
Networking and Communication |
Routers, switches, and modems |
High-speed data processing, packet switching, and protocol handling tasks |
|
Automotive Electronics |
Engine control, driver assistance systems, infotainment systems, and vehicle networking protocol |
Optimizing the functionality, efficiency, and reliability of critical systems |
|
Industrial Automation |
Robotics and process control systems |
Control, monitoring, and data acquisition |
|
Medical Devices |
Patient monitoring systems, diagnostic equipment, and implantable devices |
Signal processing, sensor interfacing, and control algorithms |
|
Aerospace and Defense |
Avionics, guidance systems, radar processing, and communication systems |
High-performance, reliable, and secure solutions for critical functions |
The primary advantages of ASICs in embedded systems include customized functionality, high performance, low power consumption, and reduced form factor and cost compared to alternatives. However, ASIC development requires significant investment in design and manufacturing, making it most suitable for high-volume production and applications where performance optimization is paramount.
Design Methods for Application-Specific Integrated Circuits in Embedded Systems
Gate array ASIC showing predefined logic cells and custom interconnections
(Source: Wikipedia user Antoinebercovici)
Various approaches and techniques are used in the design and manufacture of ASICs. The table below lists some common methods with their advantages and disadvantages.
|
ASIC DESIGN METHODS |
||
|
Method |
Advantages |
Disadvantages |
|
Full Custom Design |
– Highest level of customization and performance |
– Time-consuming and requires extensive expertise |
|
Semi-Custom Design |
– Balances customization with existing IP cores |
– Limited flexibility compared to full custom design |
|
Gate Array Design |
– Faster turnaround time compared to full custom design |
– Limited flexibility and performance compared to full custom design |
|
Standard Cell Design |
– Faster design iterations and better scalability compared to gate arrays |
– Limited customization compared to gate arrays and full custom design |
Each ASIC design method offers a unique set of advantages and disadvantages. The designer’s choice depends on factors such as the complexity of the design, time-to-market requirements, budget constraints, and customization level.
Accurate CAD Models Are Essential for ASIC PCB Design
Application-specific integrated circuits often have multiple I/O connections. Ensuring that your CAD models accurately represents all dimensions; such as pin size, spacing, and pitch angle, is critical for PCB layout design, fabrication, assembly, and operation once the board is deployed. Relying on the industry’s leading source for downloadable CAD models, as shown for the ASIC below, is the best option.
MIcrochip RE46C180S16TF programmable ionization smoke detector ASIC CAD models from UL
A clear understanding of ASIC design methods and applications will aid you in designing and developing PCBs that employ ASICs. With this knowledge, you can better source project components and devices for your embedded systems.
If you’re looking for CAD models for common components or tips on using an application-specific integrated circuit in embedded systems, Ultra Librarian helps by compiling all your sourcing and CAD information in one place.
Working with Ultra Librarian will set your team up for success to ensure streamlined and error-free design, production, and sourcing. Register today for free.