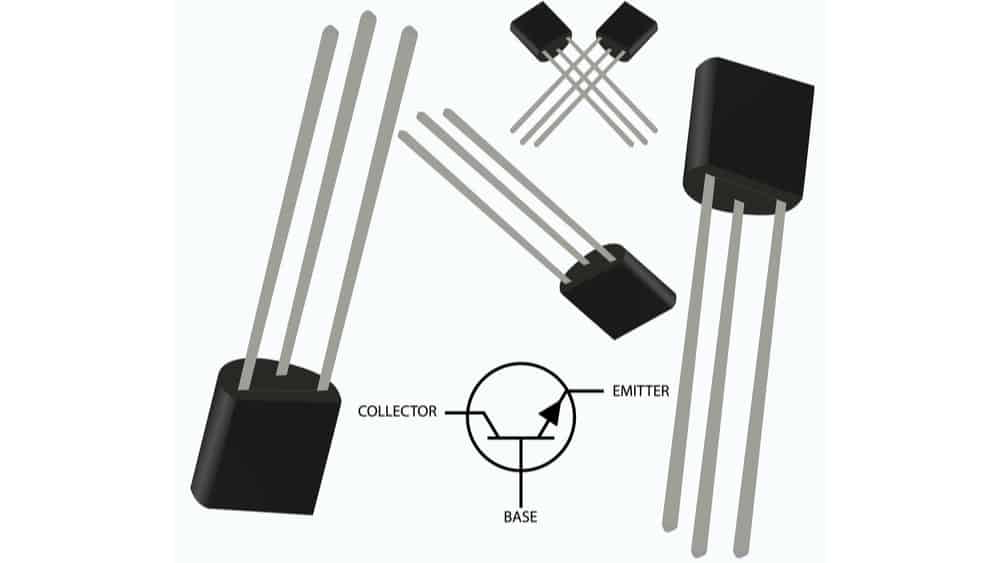
The 2N3904 is a N-type BJT and is available in the TO-92 package.
A small signal transistor is designed for low voltages and currents, not for power amplifiers. The 2N3904, registered by Motorola in the mid-1960s, is a small signal transistor used for general-purpose switching (100 mA) and amplification (100 MHz) applications. It is an NPN BJT transistor, yet is also available in a PNP configuration (2N3906). Knowing how to read the 2N3904 datasheet, which includes the common symbols for both configurations helps engineers better design for reliable amplification and switching applications.
2N3904 Datasheet Analysis
Maximum Ratings
The 2N3904 transistor has maximum ratings, as shown in the table below.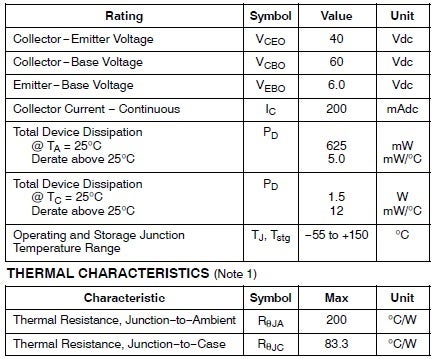
As you can see, the transistor can conduct a maximum of 200 mAdc with a maximum applied input voltage of 6 Vdc between the base and emitter. However, the device is unsuitable for high-power applications (as shown by the milliwatt-level power dissipation).
Transistor Gain
The table below shows the ON characteristics of 2N3904.
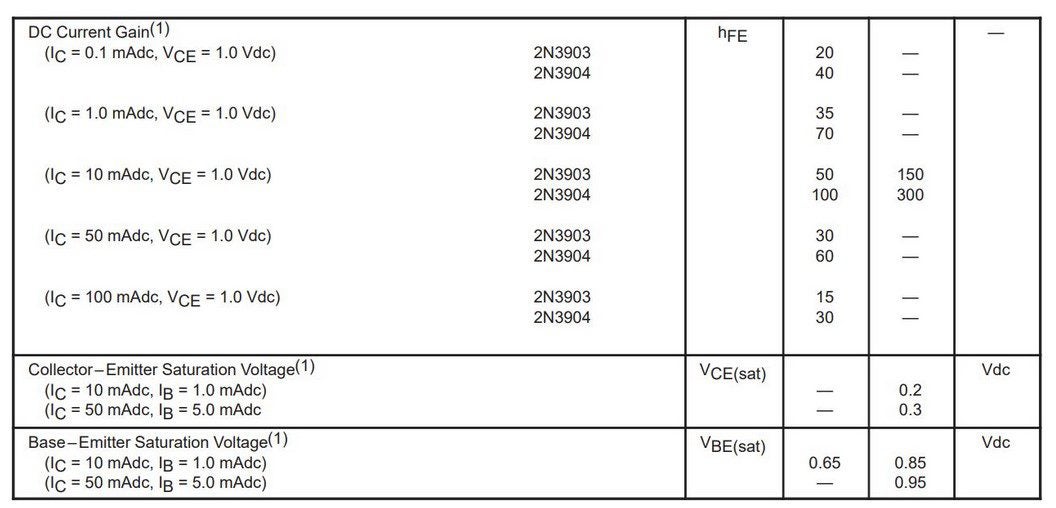
The 2N3904 datasheet lists the DC gain (hFE) of its alternative 2N3903 (PNP) in separate rows. You can see that the PNP type has 50% less gain than the NPN type, which is the biggest reason why the NPN type is so popular. The minimum gain for 2N3904 is 40 for IC = 0.1 mA, which goes up to max 300 for IC = 10 mAdc at VCE = 1.0 Vdc. At this point, the gain is ten times the minimum that the transistor gradually achieves at the end for IC = 100 mAdc at VCE = 1.0 Vdc.
This analysis acknowledges the importance of designing the transistor’s circuit for hassle-free operation despite a high gain bandwidth.
The maximum voltage drop across the device (Vce) during the ON condition can have two different values as follows:
- 0.2Vdc when the IC = 10 mA and a 1 mA current on the base (hFE = 10)
- 0.3Vdc when the IC = 50 mA and a 5 mA current on the base (hFE = 10)
Small Signal Characteristics
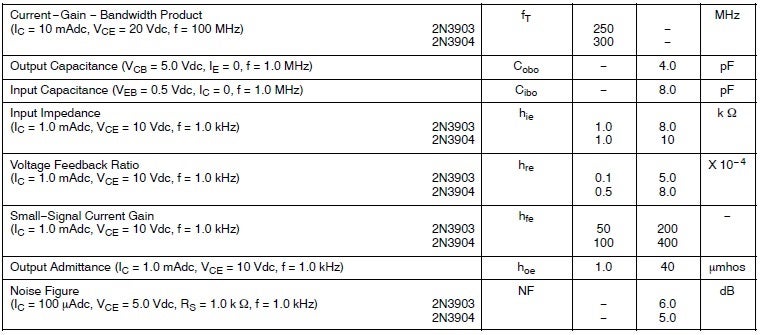
The term fT represents the frequency at which the output signal current will be equivalent to or less than the input signal current, irrespective of the set amplification. That means, at this frequency, the transistor can no longer amplify the signal.
The term NF represents the internally generated noise by the transistor due to temperature fluctuation, which should be no worse than 5 dB in this case, as per the 2N3904 datasheet. If your application is sensitive to this much noise, e.g., RF amplifiers, and requires an extremely quiet device, transistors like 2SC3324 or 2N5088 would be your ideal bet.
Switching Characteristics
Due to the transistor’s inherent capacitance (Cce, Ccb, Ceb), the current rises and falls over time. It’s not instantaneous, as the capacitor takes some time to discharge.

As per the 2N3904 datasheet, the transistor takes 35ns to rise from its initial value to 10 % of its final value (delay time) and the same time to reach 90% of its final value (rise time). The storage time indicates the time required to get the carriers out of the base of the transistors.
Applications of the 2N3904
The 2N3904 excels in the following circuit operations:
- Minimum load switches (up to 200mA) for less saturation voltage and maximum gain
- Amplifier modules such as audio amplifiers and signal amplifiers, because of their high current gain
- Automatic-switching applications
- Fast-switching applications such as pulse width modulation
- Home appliances such as TV and stereo systems
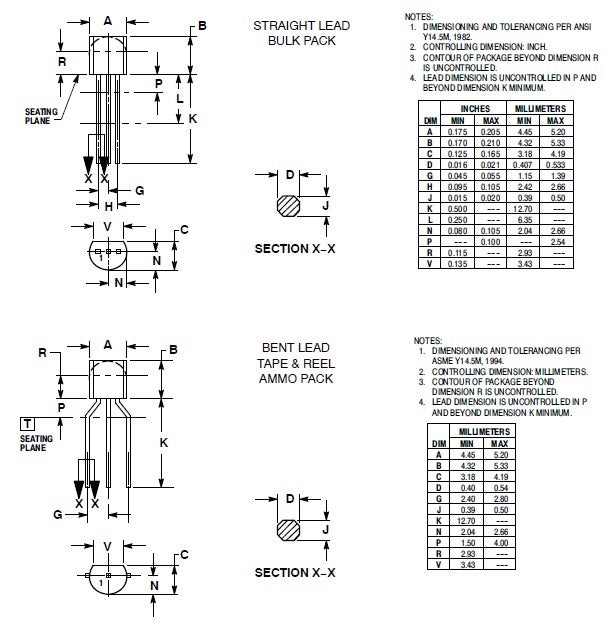
Packaging and Dimensions
The transistor is available in through-hole and SMD packages, TO-92, shown below, and SOT-23 and SOT-223, respectively.
2N3904 Equivalent Components
Depending on cost or availability concerns, designers may seek an alternative to the 2N3904. The key to identifying a replacement is determining which aspects of the 2N3904 are necessary for the application. As shown, several metrics are available to quantify amplifier action; a good first step is to indicate or rank the characteristics most essential and compare these to similar components.
2N3904 and Alternatives Comparison | |||||||
Transistor | Type | Amplification | Current | Voltage | Speeds | Packages | |
2N3904 | NPN BJT | Low-power | Low | Moderate | Moderately high | TO-92, SOT23, SOT223 | |
2N2222 | NPN BJT | Low-power | Moderately low | Moderate | Moderately high | TO-18, TO-92, SOT23, SOT223 | |
2N2907 | PNP BJT | Low-power | Moderate | Moderate | Moderately high | TO-18, TO-92, SOT23, SOT223 | |
2N3055 | NPN BJT | Moderate-power | Moderate | Moderate | Moderately high | TO-3, TO-220, SOT93 | |
BC548 / BC848 | NPN BJT | Low-power | Low | Moderate | Moderately high | 548: TO-92 848: SOT23 | |
Ultra Librarian Makes Component Research a Breeze
Going through the 2N3904 datasheet is imperative to best understand each package type’s pin layout and design configuration list. However, collecting all that information from different sources could take time. Ultra Librarian has a well-optimized online library that saves time on component research. Just type a part number or keyword into the search box, and the library will fetch essential details; such as the datasheet, component availability status, price, and CAD models available—all in one place.
Working with Ultra Librarian sets up your team for success to ensure streamlined and error-free design, production, and sourcing. Register today for free.