Switching is one of the most critical functions in an electrical or electronic circuit. Switching is starting or stopping the current flow between a source component and a load within the same circuit or between two interconnected circuits. As switching is essential, it is vital to know the differences between the most common types of switch components: relays and transistors.
For high-speed switching, transistors should be used. However, relays are the best option for high-power applications, especially when isolation between the switch control and load is essential. Relays are applied in a wide range of applications. One of these application areas is defense systems. These relays must meet special requirements, and Teledyne Relays is well-known for manufacturing components that reach the high-performance bars that the military demands.
When choosing devices for your design, Teledyne Relay datasheets are reliable sources to help ensure your design will exhibit the quality defense systems must have.
Requirements for Military Grade Relays
Relays, which may be electromechanical or solid state, are electromechanical devices. They are often classified according to default contact configuration as normally open (NO), normally closed (NC), or common contact (COM). Another common classification is based on the number of control switches or input circuits, known as poles, and load or output circuits, or throws. These include single pole single throw (SPSW), single pole double throw (SPDT), double pole single throw (DPST), and double pole double throw (DPDT) types.
A special classification of the relay is military-grade, which Teledyne Relays specializes in producing. These relays must be able to perform their intended function in the often hazardous environments that military systems operate in. Therefore, relays are put through several tests to ensure their versatility and reliability, such as the ones listed below.
|
TESTING STANDARDS FOR MILITARY GRADE RELAYS |
|
|
Standard |
Purpose |
|
Gives the requirements for encapsulated or hermetically sealed solid state relays (SSRs) and covers microelectronic, semiconductor, and passive devices. |
|
|
Defines the electric power requirements for utilization with aircraft systems. Includes specifications, test procedures, characteristics, and standard compliance requirements. |
|
The above standards are comprehensive and require extensive inspections and testing to validate compliance. The Teledyne Relays datasheets include descriptions, data and information for the various series of DC and AC relays the company makes that adhere to these standards.
Teledyne DC Relays for Defense Applications
Teledyne Relays makes several series of DC relays, which are described below.
Series LD Relays
Series LD relays are through-hole mounted and designed for high voltage–up to 270V DC–applications, employ optical isolation between input and output, satisfy MIL-STD-704, and meet the requirements of MIL-PRF-28750.
Series CD Relays
Teledyne series CD relays come in both through-hole and surface mount packages, are designed for fast switching applications, optically isolated, satisfy MIL-STD-704 for 28V DC, and meet MIL-PRF-28750 requirements.
Series HD Relays
Also designed for fast switching are the HD series relays, which are through-hole, optically isolated, comply with MIL-STD-704 for 28V DC, and meet MIL-PRF-28750 requirements.
Series KD/LD Relays
The KD/LD series relays are through-hole mounted, include short-circuit protection, employ optical isolation, satisfy the 28V DC requirements for MIL-STD-704, and adhere to MIL-PRF-28750 requirements.
KD44CF Series Relays
KD44CF relays also include short-circuit protection, are through-hole mounted, optically isolated, MIL-STD-704 for 28V DC compliant, and meet MIL-PRF-28750 requirements.
M33-2N Series Relays
M33-2N series relays are fast switching, transformer isolated, optically isolated, through-hole, and adhere to MIL-PRF-28750 requirements.
Teledyne Military Grade AC Relays
Teledyne also makes AC relays for military applications, as listed below.
Series 2305115-2T Relays
Series 2305115-2T relays are 3ɸ AC relays for low voltage (47-440 Hz) applications, optically isolated, epoxy mounted, and MIL-STD-704D compliant.
Series 652 Relays
Series 652 relays are designed for power switching, employ terminal mount, are designed for low EMI, and MIL-STD-28750 qualified.
Series 682 Relays
Series 6825 relays are optically isolated, low EMI, through-hole, and MIL-STD-28750 qualified.
For additional information in choosing the best Teledyne series relay for your application, see the Military Solid State Relay Selection Guide.
Effectively Using Teledyne Relays Datasheets for Your Design
In addition to the information in the previous section, the Teledyne Relays datasheets include block diagrams, pinouts, electrical characteristics, and other vital data to aid you with the PCB layout for your relay application board. These reference documents also provide information for creating footprints for your layout.
Building component libraries from scratch, especially footprints, is not recommended. These part representations must be accurate and adhere to industry PCB design standards for manufacturability, design for manufacturing (DFM), and design for assembly (DFA) rules and guidelines from your CM. A better option is to utilize verified CAD data and models, as shown below.
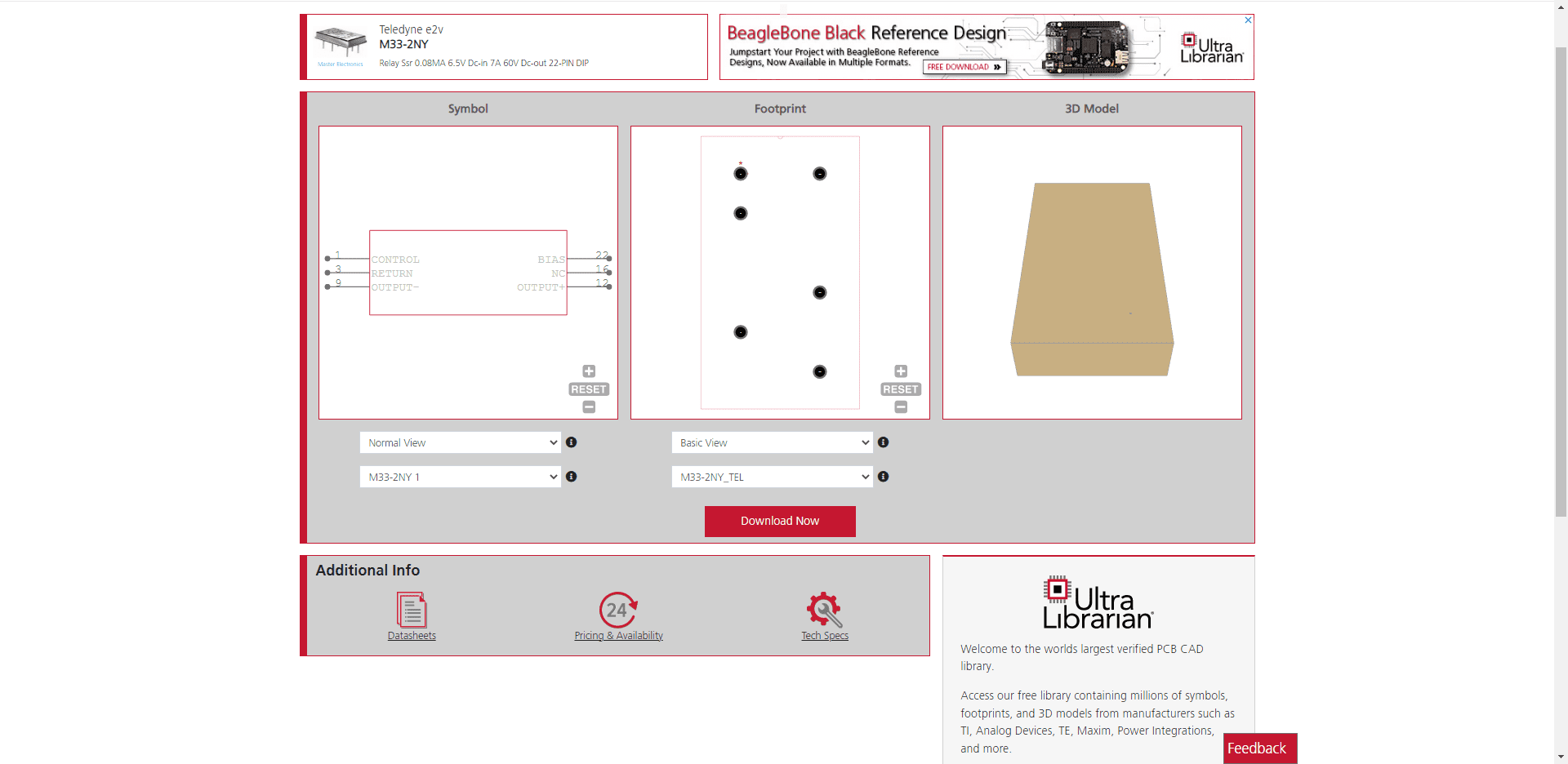
M33-2N Series relay CAD models from UL
Leveraging data and information from the Teledyne Relays datasheet and accurate CAD models from a trusted online component library source is the best strategy for optimizing your PCBA design and development process.
If you’re looking for CAD models for common components or design tips to best use information from technical documents like the Teledyne Relays datasheets, Ultra Librarian helps by compiling all your sourcing and CAD information in one place. Working with Ultra Librarian sets up your team for success to ensure streamlined and error-free design, production, and sourcing. Register today for free.