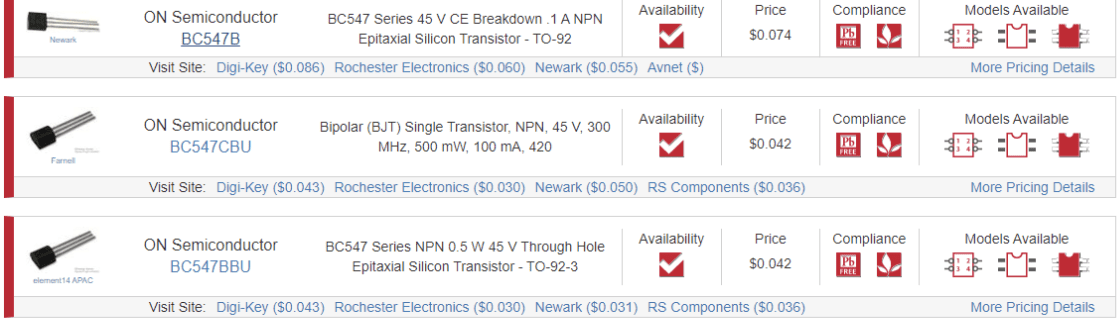
The BC547 is one component in a line of NTN silicon transistors provided by ON Semiconductor. All of the transistors in the BC5xx line are very similar, but each has slightly different technical specifications. The BC547, according to its datasheet, has 8 variants. Each of these variants is optimized for different voltage and noise levels, although they have the same basic physical structures as other components in the BC5xx line. The key difference between components in the BC5xx line is their different tolerances for base, collector, and emitter voltages.
The BC547 Datasheet
The BC547 datasheet is unusual because instead of describing a single component, it describes a large group of related components, including the BC547. From the BC546 through the BC550, the datasheet focuses on the similarities between these components. Yet, it does also bring the reader’s attention to some important differences. The datasheet is valid for all members of the BC5xx line, unless it explicitly mentions important differences. In addition, the datasheet is unusual compared to most, as it doesn’t go into the same level of technical detail as many other datasheets. The datasheet only comprises a concise 8 pages; most datasheets are usually around a minimum of hundred pages.
Similarities in the BC5xx Line
All members of the BC5xx line, including the BC547, are NTN silicon transistors. They look like an elongated jellyfish, with 3 prongs to carry current and a base to coordinate current flow through the prongs. Depending on the BC5xx line variant, these prongs can be bent or straight. The BC547B, a particularly common component, has straight prongs. The prongs intersect the base close to its top surface, rather than having the base centered vertically. All the transistor variants are approximately the same size, at 5 mm in width and 20 mm in length, but some may be slightly smaller or larger.
The BC547, like the other members of its line, can function over a wide range of temperatures, from -65 to 150 degrees Celsius. It can be included in a variety of general purpose projects as an amplifier or switch. Forcing the transistors to operate in an environment hotter than 150 degrees Celsius could quickly damage them. They are rated for 100 mA of current in the collector base and can dissipate 500 mW of power. Designers should not put undue stress on any of the components in the BC5xx line—although they are rated well, they function best at lower levels of stress.
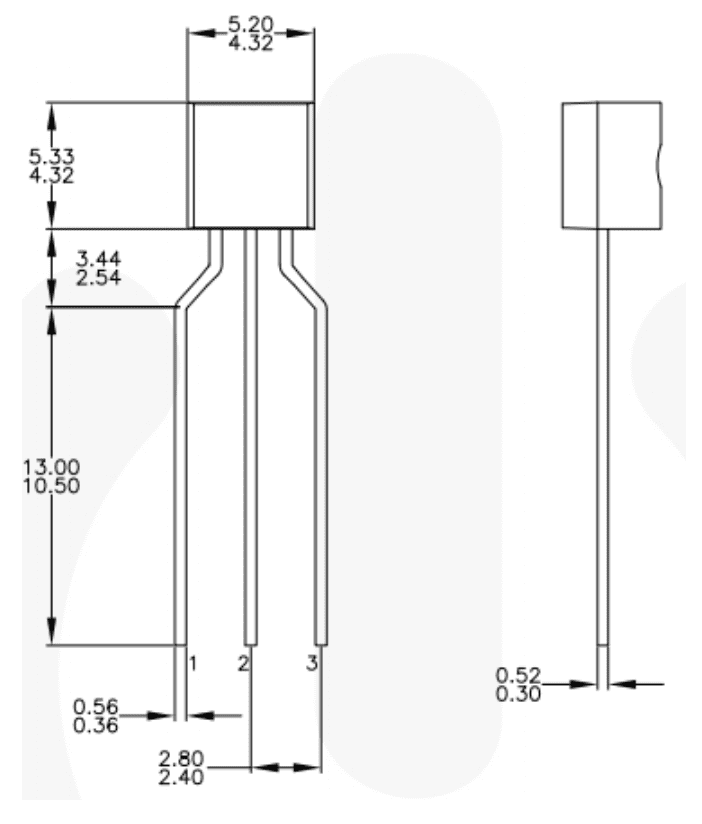
Differences in the BC5xx Line
The BC547 is, in general, a transistor variant that balances the minimum and maximum capacities of the BC5xx line. It’s rated for 50 volts of collector base voltage—equal to the BC550, less than the BC546, and more than the BC548 and BC549, both of which have the least voltage tolerance. This trend among BC5xx line components is also true with collector emitter voltage. The BC546 can handle the highest voltage, while the BC548 and BC549 can handle the least. The BC547 and BC550 are in the middle. However, this trend changes with emitter base voltage—both the BC546 and BC547 can handle more voltage than other components in the BC5xx line.
The BC5xx line has three different current classifications: A, B, and C. An A classification can handle the least current, while the C classification can handle the most. The BC546 and BC547 both have variants able to handle all three current classifications, while the other members of the BC5xx line are used specifically for higher current loads (but not necessarily higher voltages).
Ultra Librarian provides multiple BC547 variants for designers, as well as an extensive selection from the BC5xx line, to give engineers unprecedented design flexibility. Working with Ultra Librarian takes the guesswork out of preparing for your next great device, and puts your ideas on the road to success. Register today for free.