
See how you can convert between the digital and analog world with the MCP4725.
Converting between analog and digital signals is essential for electronics to interface with the real world. Many MCUs and other processors include analog to digital converters (ADCs) and/or digital to analog converters (DACs) built into a design. However, some MCUs are very lightweight and will only include the bare essentials needed to interface with a few peripherals. For these MCUs to interact with the real world, separate components are needed to capture or generate analog signals in a digital device.
The MCP4735 is one such external ADC used for analog signal generation as required by a host controller. With a simple 2-wire digital interface, the MCP4735 gives designers a simple way to incorporate features like arbitrary waveform generation and signal transmission without the need for a specialized, integrated transceiver. Although an MCP4725 datasheet can be tough to find, we’ve compiled the resources you need to understand the MCP4725 in this article.
What’s in the MCP4725 Datasheet?
The MCP4725 is a DAC manufactured by Microchip. This 12-bit DAC includes built-in EEPROM memory for storing device configuration and desired input data. This component comes in four different SMD package styles for easy mounting to a PCB. While it can find a home in industrial applications, it is marketed closer to automotive or sensing applications, such as:
- Sensor driving or calibration
- Closed-loop servo motor control
- Portable instrumentation
- Data acquisition systems
Key specifications for the MCP4725 and DAC components are shown in the table below.
| Specification | Value |
| Max. drain current | 41 A continuous DC, 160 A pulsed |
| Digital interface | Two-wire I2C:
|
| Output range | Rail-to-rail |
| Settling Time | 6 μs |
| Voltage reference | Provided externally |
| Differential nonlinearity | No more than 0.2 of LSB |
| Operating temperature | -55 °C to 125 °C |
| Packages | DFN, SOT-23/SOT-23-6 |
| EEPROM register size | 14 bits (2 for configuration, 12 for input) |
Using the MCP4725 DAC
Programming
The internal EEPROM is useful, as the required output level can be stored in non-volatile memory. When the device is initially powered on, the code stored in the EEPROM is loaded and the device outputs the analog level setting with the programmed configuration settings. This means the MCP4725 will start outputting the required voltage on startup without requiring reprogramming. The device will output immediately, even if the host controller MCU does not receive power or has gone into sleep mode.
Power Output
The MCP4725 is specifically marketed as a low-power DAC, and the output can be switched off by setting the configuration bits via the I2C interface. Although there is no specific absolute maximum power rating in the MCP4725 datasheet, the component will output from rail-to-rail at up to 25 mA current.
Additional Passives
To properly use the MCP4725, some external passive components are needed to ensure proper operation. These include:
- Pull-up resistors on the I2C line to set the appropriate level on the SCL and SDA pins.
- Decoupling at the supply pin to minimize ripple on the power rail during switching.
Because the output level is stored as a 12-bit number in the device’s memory, the MCP4725 is best for outputting at DC level unless the 12-bit level register is continuously programmed via the I2C bus.
Power Down Control Circuit
The output can be powered down with an external control circuit, rather than setting the output to zero via the I2C interface. Using the external control circuit is preferable, as the output can be set in non-volatile memory and modulated to zero with a simple 4-channel digital switch circuit, even if the system’s host controller goes into sleep mode. The diagram below shows the placement and implementation of an external control circuit.
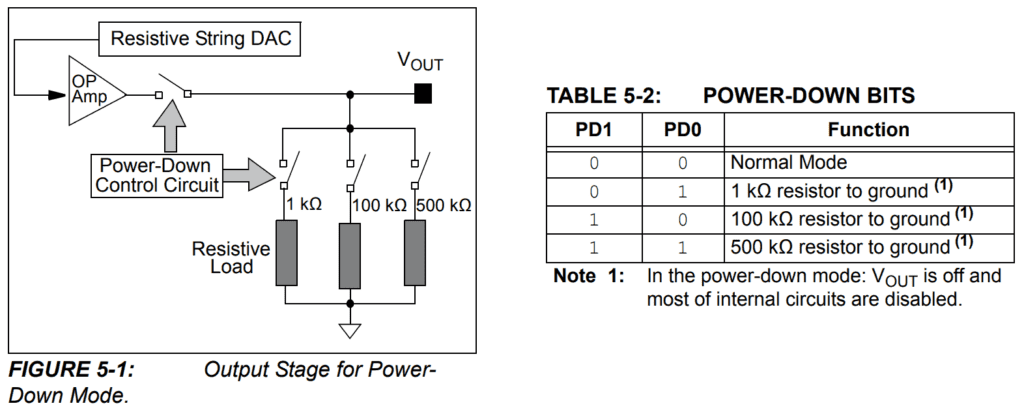
Control circuit implementation for the MCP4725 (from the MCP4725 datasheet).
An Alternative to the MCP4725 DAC
The part number “MCP4725” is not exactly a generic part number, but one component from Rohm Semiconductor markets itself as part of the MCP4725 series and just happens to be a DAC. Other companies manufacture their own components that are comparable to the MCP4725 in terms of cost, package size, and capabilities.
One alternative from Microchip is the MCP4728 DAC. This component is also a 12-bit DAC, but it has 4 channels and comes in a 10-pin MSOP T/R package. This part is marketed towards the automotive industry and products requiring high channel count with some level of simple programming. This component is programmable over I2C, and also includes an internal reference voltage source (2.048 V) and an EEPROM so the configuration can be saved.
If system size is a concern, you’re better off just using an MCU that integrates the DAC into the die. These MCUs will offer other useful features, such as DACs, comparators, plenty of GPIOs, and standard digital interfaces (I2C, UART, and SPI are typical). Whether you want to use an MCP4725 or an alternative component, you can use an electronics parts search tool to find these components.
When you’re looking for an MCP4725 datasheet or other analog components’ technical documentation, use the electronics search engine features in Ultra Librarian. You can find component data for your components with verified CAD models that can be imported into popular ECAD applications. You’ll also have access to sourcing information from worldwide distributors.
Working with Ultra Librarian sets up your team for success to ensure any design is going through production and validation with accurate models and footprints to work from. Register today for free.








